Prepping basics: 3 Alternative power solutions if you want to go off-grid
09/08/2019 / By Melissa Smith

To live off-grid is to stop relying on the traditional power lines and choosing your own power source. There are many off-grid power generator solutions that can power heat and air units, refrigerators, and other electronic devices. People who embrace living off-grid have discovered ways to utilize other power solutions. Here are three main options. (h/t to BlueYurtFarms.com)
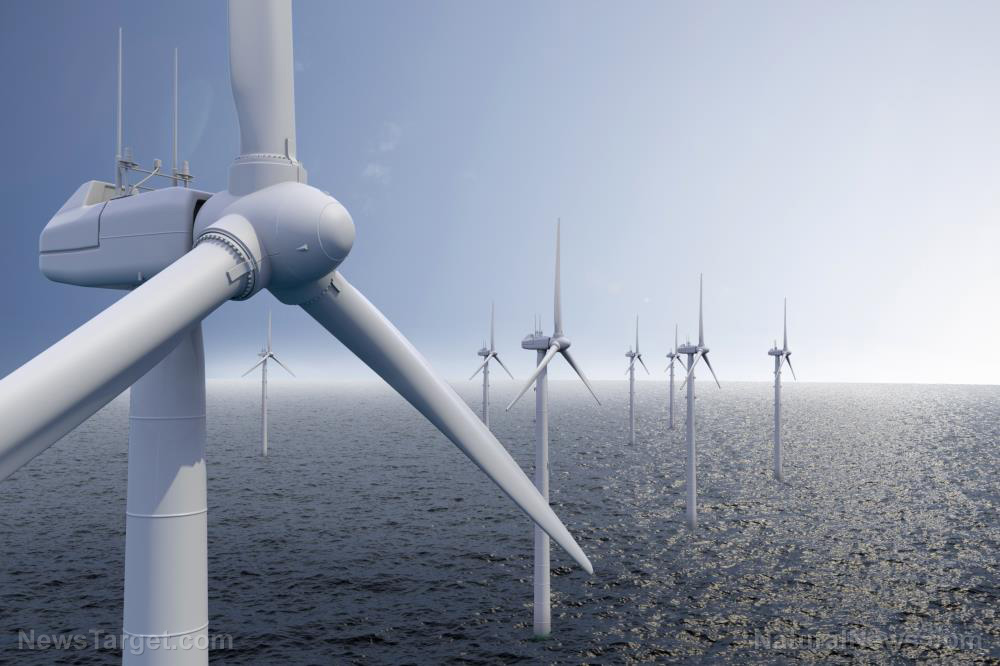
Wind power
This type of power uses the wind to generate power. A propeller blade spins as the wind blows through it. These blades capture kinetic energy and transfer it to a generator inside the rotating housing behind the blades. From this, it produces electricity.
Generating electricity from residential-sized wind turbines is a great option for off-grid energy. You can contact your local weather service to check on the average wind speed in your area. By knowing the average wind speed ranges, you can calculate how much electricity a given system can produce. Note that wind speeds on a particular lot can vary significantly from regional averages depending on local topography.
You also have to consider the size of a turbine. A 400-watt wind turbine uses about a four-foot-diameter rotor; it is big enough to account for a few appliances. To power most or all appliances in a house, you need a 23-foot turbine that is mounted on a tower more than 100 feet tall. However, this isn’t ideal if you live in a town or on a small plot. Keep in mind that your location needs to have a consistent stiff breeze to generate electricity from this. If the wind doesn’t blow, the turbine stays still, and the electricity isn’t generated.
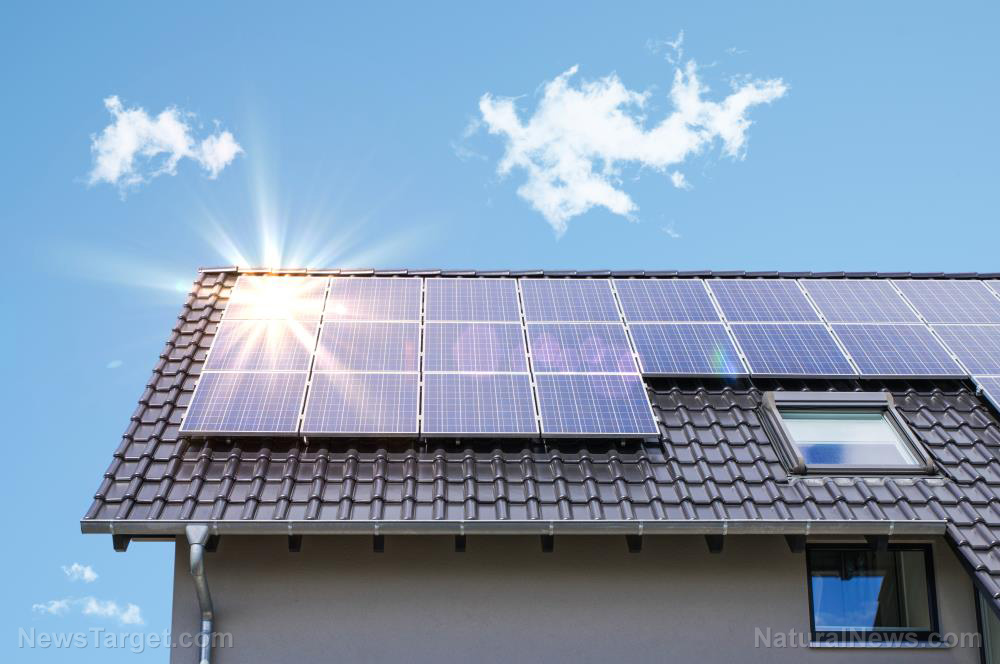
Solar power
Solar power uses the sun to generate electricity through photovoltaic solar panels, which are often installed on the roof of an off-grid home. These solar panels store sunlight in a battery, where it will stay until it is needed. Solar power can provide lots of electric power, especially if you get a lot of sun exposure where you live. Solar power is also easier to maintain than wind power as it has no moving parts. However, if you choose this power source, be prepared for the expenses. It is rarely cost-effective to power an entire home with solar energy. (Related: Solar vs. Wind Power: Which Is the Power Of the Future?)
Generator power
Generators can be used both on and off the grid. If you want to live off-grid, there are portable ones available. A quiet generator can be used to power homes in all locations using natural gas, solar power, diesel, and gasoline. Some generators are designed to work using more than one type of fuel, depending on the availability in your area.
Which is the best option?
All options have their pros and cons. The most efficient option is solar power. As mentioned, it has fewer moving parts and requires little maintenance. On the other hand, wind provides the most power output. About 60 percent of output from a wind source can be converted into energy, compared to only 20 percent from a solar output. However, wind turbines take up a lot of space and cannot easily be moved from one place to another. Lastly, a generator can provide enough power for most homes and you only need fuel to power them.
Solar power is actually cheaper than wind power in terms of a renewable source of energy – it’s for the installation that you will need a huge amount of money. It could cost you up to $29,000 for solar panel installation, depending on the size of your home. Generators may be the cheapest option as you can purchase one for a few hundred dollars.
Like may aspects of the prepping lifestyle, off-grid living requires planning and preparation, but the results will be worth your hard work.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: bug in, bug out, electricity, generators, green energy, green living, homesteader, homesteading, off grid, Off-the-grid living, power grid, power solutions, power sources, preparedness, prepper, prepping, renewable energy, self-reliance, self-sufficient, solar energy, solar panels, solar power, survival, survivalist, sustainable living, wind energy, wind power, Wind Turbines
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
PowerGrid.News is a fact-based public education website published by Power Grid News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Power Grid News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.